A Simple Guide to Supporting Data Publishing
As an academic publisher, promoting data sharing is essential for advancing research and ensuring that findings are accessible to the scientific community. This guide outlines key recommendations and considerations for journals. It aims to assist you in helping researchers successfully publish the research data underlying their results reported in your journals and to ensure that this data is properly associated to the respective article.
This guide is based on our standards for data publishing for academic publishers. You can view the full list of standards at the end of this article.
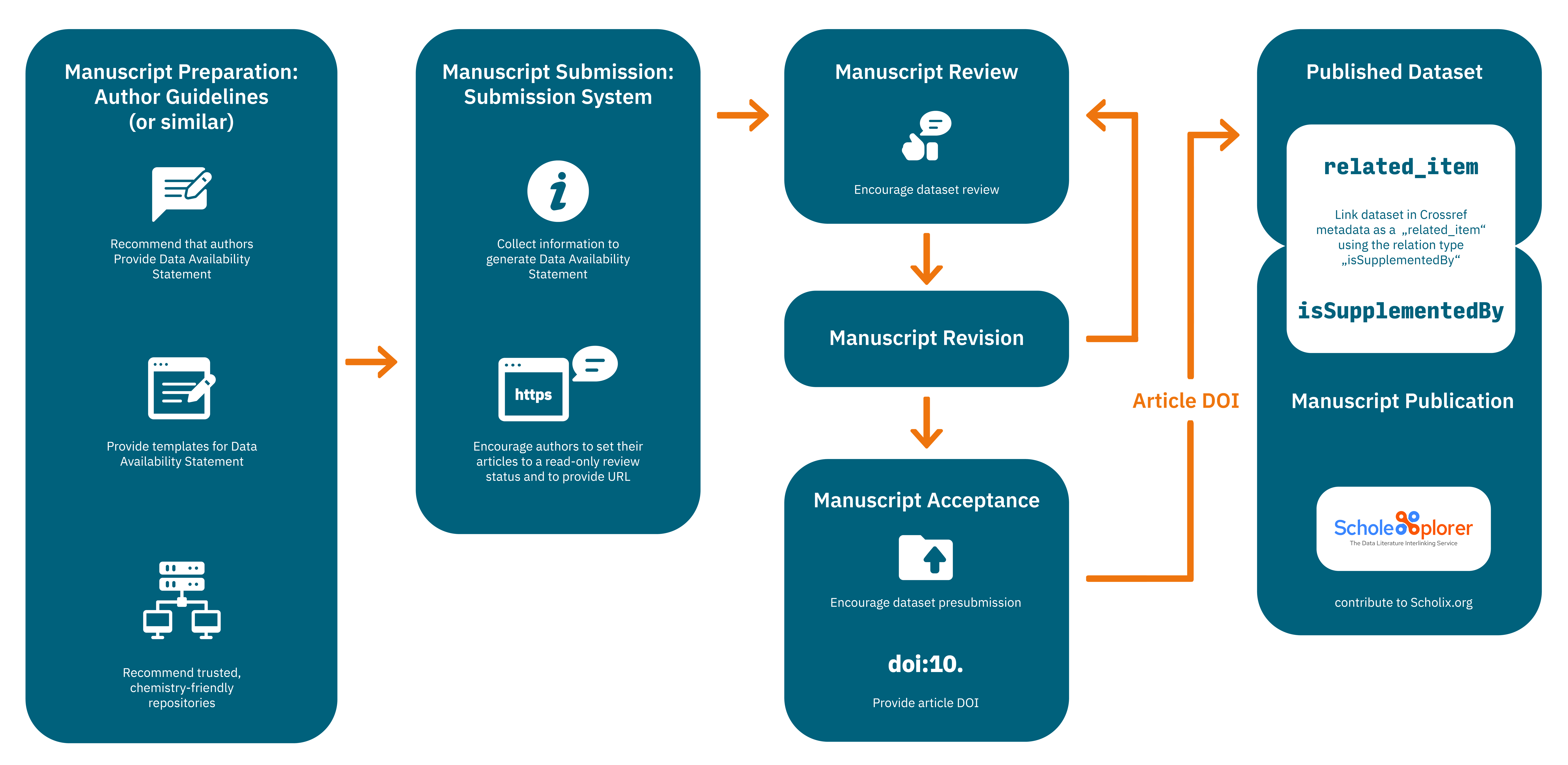
1. Recommend Trusted, Chemistry-Friendly Repositories
To assist authors in selecting well-established and community-specific repositories for their research data, it is important for journals to recommend trusted chemistry-friendly repositories. This information should be included within the author guidelines or data policies to assist researchers during the publication process.
2. Include Data Availability Statements
Journals should encourage authors to provide a data availability statement in their manuscripts. To facilitate this, templates should be made available in the journal's author guidelines or similar sections. These templates help authors correctly submit underlying data with their manuscript while effectively communicating how to find and access the data by including DOIs or other PIDs, thereby enabling adherence to FAIR principles (e.g., A1.
3. Integrate Data Availability Statements into Submission Systems
Journals should incorporate a data availability statement feature into their manuscript submission systems. Once a template has been selected by the submitter, it should remain editable so authors can add additional details about what data are included in their dataset. The submission system must require necessary information such as DOI (specified as either a DOI name or URL), repository name, third-party ownership details if applicable, reasons for restricted access, and instructions on how to access datasets based on the chosen template.
4. Link Datasets to Articles in Crossref DOI Metadata
Journals should enhance Crossref DOI metadata by linking articles to datasets using information from data availability statements. By incorporating DOIs and repository names into Crossref metadata according to FAIR principles, journals establish structured links between article DOIs and dataset DOIs—ensuring both humans and machines can interpret these relationships effectively.
In agreement with Crossref's documentation on linking datasets, use the relationship type isSupplementedBy.
XML Example:
<rel:program name="relations">
<rel:related_item>
<rel:description>
Dataset in <<<repository name>>>.
</rel:description>
<rel:inter_work_relation relationship-type="isSupplementedBy" identifier-type="doi">10.prefix/suffix</rel:inter_work_relation>
</rel:related_item>
</rel:program>
5. Encourage Pre-submission of Datasets
Journal author guidelines should explicitly encourage pre-submission of datasets prior to manuscript submission—similar to current practices for crystallographic data published in CSD with CCDC. Early publication facilitates manuscript workflows as DOIs are registered beforehand. This can, for example, enable automated DOI quality checks.
A potential drawback is that researchers cannot link their dataset directly to an unpublished manuscript until a DOI has been assigned, usually after its publication, thus requiring manual updates to the dataset metadata post-publication.
6. Include Research Data in Review Processes
Journals should encourage inclusion of research data during peer review processes by allowing datasets labeled as under review. These datasets have reserved DOIs but are not yet published; they provide editors and reviewers access via a URL while maintaining integrity throughout evaluation.
7. Require Publication of Datasets Under Review Prior to Article Publication
As mentioned above, to streamline automated workflows linking datasets with published articles through respective PIDs, journals must require that datasets marked under review be published before associated articles are released. Authors should receive clear communication regarding this process upon acceptance of their manuscripts.
Communication Tips:
Alongside acceptance notifications, journals should provide authors with corresponding article DOI so they can include this metadata prior to dataset publication.
8. Utilize Scholix.org Framework
Journals should leverage Scholix as a framework for enhancing links between scientific literature and research data—thereby improving interoperability across connected digital objects through Scholix hubs like DataCite or OpenAire. This allows academic publishers to discover relevant datasets even after articles have been published.
Standards
- Journals should recommend trusted, chemistry-friendly research data repositories.
- Journals should recommend that authors provide a data availability statement. Author guidelines should also provide templates for illustration
- Journals should add a data availability statement to published articles and collect the necessary information through their submission systems.
- Journals should use the information available in data availability statements to enhance Crossref DOI metadata by linking articles to datasets.
- Journal author guidelines should explicitly encourage pre-submission of datasets.
- Journal author guidelines should explicitly encourage research data to be included in the review process.
- Journal author guidelines should require that datasets with status under review to be published prior to the publication of the associated article.
- Journals and publishers should use Scholix.org.
Main authors: ORCID:0000-0003-4480-8661, ORCID: 0000-0002-6243-2840